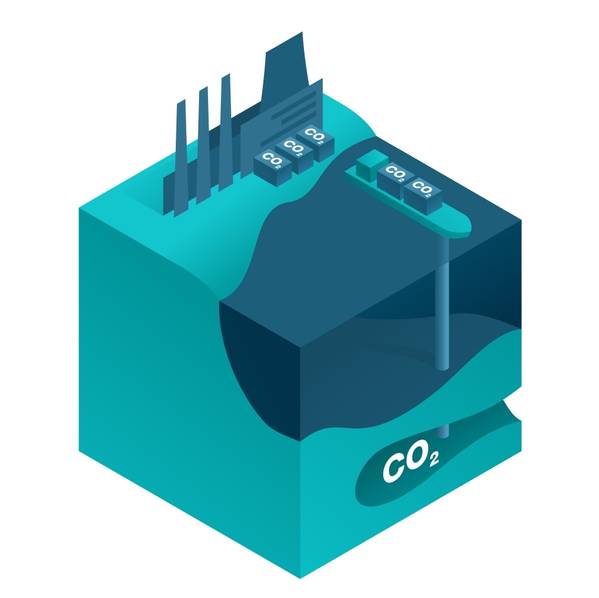
Australia plans to scale up its capability for offshore carbon capture and storage (CCS) and will shortly seek public feedback on a new round of greenhouse gas storage acreage, the country’s resources minister said on Tuesday.
The country, one of the world's largest liquefied natural gas (LNG) exporters, is banking on CCS technology to decarbonize its industries and continue expanding its LNG production to meet demand from top buyers such as Japan and South Korea.
"Last year, I announced the first two new offshore greenhouse gas storage permits in 14 years, but there is scope to dramatically scale up Australia’s offshore CCS capability," Resources Minister Madeline King said at an industry conference.
The government will shortly start public consultation on a new round of greenhouse gas storage acreage, she added.
Australia has also started looking at formulating policy on CCS projects for broader industrial use, King said.
"We want a regulatory system for offshore CCS that is robust and responsive, and positions Australia’s resources sector to bring new CCS projects online," she added.
Australia aims to cut carbon emissions by 43% by 2030, and reach net zero by 2050. The country is home to the world's largest commercial CCS project, Gorgon, run by Chevron Corp, which has struggled to hit capacity.
The Australian government's CCS push comes in the wake of Washington's Inflation Reduction Act, which provides big incentives for CCS, and Britain's 20 billion pound ($24 billion) investment in such projects over the next two decades.
The Australian Petroleum Production and Exploration Association (APPEA) wants to work with the government to develop a national carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) strategy, provide policy direction and prioritize carbon management hubs, its chair Meg O'Neill told the conference.
Carbon emissions are captured and stored at a site to prevent its release into the atmosphere. Captured CO2 usually is permanently stored underground, but CCUS reuses the CO2.
Environmental groups oppose CCS, saying it will unnecessarily prolong fossil fuel use.
($1 = 1.4743 Australian dollars)
(Reuters - Reporting by Emily Chow; Additional reporting by Renju Jose; Writing by Florence Tan; Editing by Sonali Paul)